Abstract
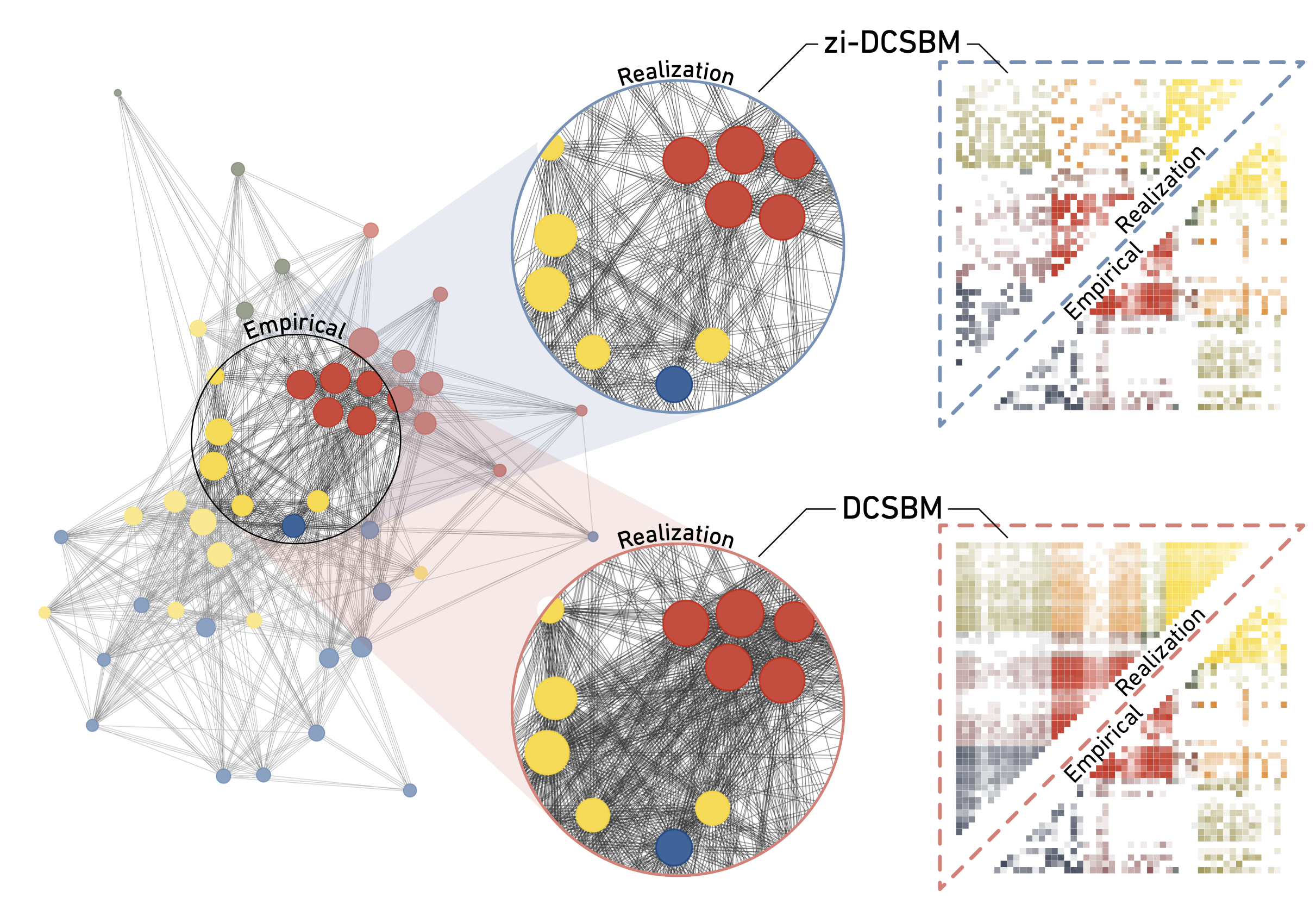
Real-world networks are sparse. As we show in this article, even when a large number of interactions is observed most node pairs remain disconnected. We demonstrate that classical multi-edge network models, such as the G(N,p), configuration models, and stochastic block models, fail to accurately capture this phenomenon. To mitigate this issue, zero-inflation must be integrated into these traditional models. Through zero-inflation, we incorporate a mechanism that accounts for the excess number of zeroes (disconnected pairs) observed in empirical data. By performing an analysis on all the datasets from the Sociopatterns repository, we illustrate how zero-inflated models more accurately reflect the sparsity and heavy-tailed edge count distributions observed in empirical data. Our findings underscore that failing to account for these ubiquitous properties in real-world networks inadvertently leads to biased models which do not accurately represent complex systems and their dynamics.